UCSD Rady Children's Biorepository
- About
- Services
- Biospecimen Lifecycle
- Contact
- Biorepository Process
- Resources
| Pre-Acquisition - biospecimen Molecular Integrity Antibiotics and other drugs |
|---|
| Anesthesia: Type and Duration |
| Arterial clamp time |
| Blood loss pressure variations |
| Blood and Fluid administration |
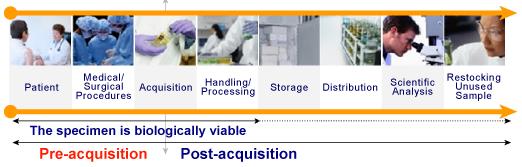
| Patient - The biospecimen exists in situ within the specific biologic context of the patient. |
|---|
| RCHSD Admission |
| COTA |
| Consented COTA Scan EMR? |
| Daily List of Consented EPIC? |
| Medical/Surgical Procedures |
|---|
| Examples include administration of antibiotics, anesthesia and other drugs. At this point anesthesiologists, nurses, and doctors may introduce variables into the procedure that change the biologic context of the "specimen" and, as a result, cause dynamic changes in the molecular profiles within the "specimen." |
| Warm Ischemia Time < 30 Minutes |
| Cold Ischemia Time 30 min < 2hr |
| On call transport specimen |
| Rapid Triage of Specimen |
| Acquisition |
|---|
| Various methods of acquiring the "specimen" may introduce specific types of stress or trauma to the living specimen. Examples include time delays (from handling to delivery), and packaging (changing exposure to desiccation or oxidation.) |
| Unique study number Barcoding |
| Collection supervised by Rady Children's Pathologists |
| Asceptic technique |
| No thaw/Freeze Cycle - Aliquot |
| Handling/Processing |
|---|
| Preparation variables introduced prior and during biologic stabilization of the specimen include: time @ RT, RT, type and time in fixative, method & rate of freezing, size of specimen aliquots. Human involvement contributes to this process. |
| Flash Freezing: LN2, OCT |
| Diseased tissue: Cancer/Non-cancer |
| Adjacent non diseased tissue |
| Controlled fixation |
| Post-Acquisition |
|---|
| Transport and Handling |
| Room Temp and Time spent at room temperature |
| Freezing - storage temperature |
| Fixative Type and Time spent in fixative |
| Quality Control/Assurance |
|---|
| H&E section of all banked tissue |
| Review by board certified pathologists |
| Correlate and Verify pathologic diagnosis |
| Viable Tumor content score |
| Bioinformatics |
|---|
| Velos/eResearch/eSample |
| Clinical data |
| Sample tracking |
| Inventory control |
| Storage |
|---|
| Variables include storage temperature, duration, progressive dehydration, desiccation and oxidation may contribute to this process. |
| CryPlus LN2 Storage |
| -80C Biomedical |
| Freezer Monitored 24/7 |
| Emergency Response on-call |
| Back up power and LN2 |
| Distribution - Variation sin transport may lead to alterations in the specimen. Package, transport and receiving all contribute to this type of variations. |
|---|
| Access to materials electronic request |
| Investigator Application Instructions Agreement Package |
| Biobank Committee review and approval |
Different methods of analysis for various classes of biomolecules may be affected by any of the factors already mentioned. Even with a single analytical method, each individual investigator and technician involved in the specimen analysis may contribute to such variation.
Restocking
Environmental variables may be introduced through the return of unused samples from research laboratories to storage.
Effects on clinical outcomes:
• Morphological analysis/diagnosis
• Skewed clinical chemistry results
• Potential for incorrect therapy when diagnostic is paired with therapeutic (e.g., HER2)
Effects on research outcomes:
• Variations in gene expression
• Variations in post-translational modification (e.g., phosphorylation status)
• Potential for misinterpretation of artifacts as biomarkers